TLDR: 2D Lidar, short for Light Detection and Ranging, uses laser beams to measure distances and create maps of environments. It's highly valued in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and mapping due to its precision and versatility. However, its performance can be affected by environmental conditions and it offers less depth information compared to 3D Lidar systems.
What is 2D Lidar?
2D Lidar is a sensor technology that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure variable distances from a sensor to a target or surface. By rapidly sending out laser pulses and measuring how long it takes for the light to return after hitting an object, it calculates distances accurately. This technology creates a two-dimensional representation of the area it scans, which is crucial for applications requiring detailed spatial awareness and mapping.
How Does 2D Lidar Work?
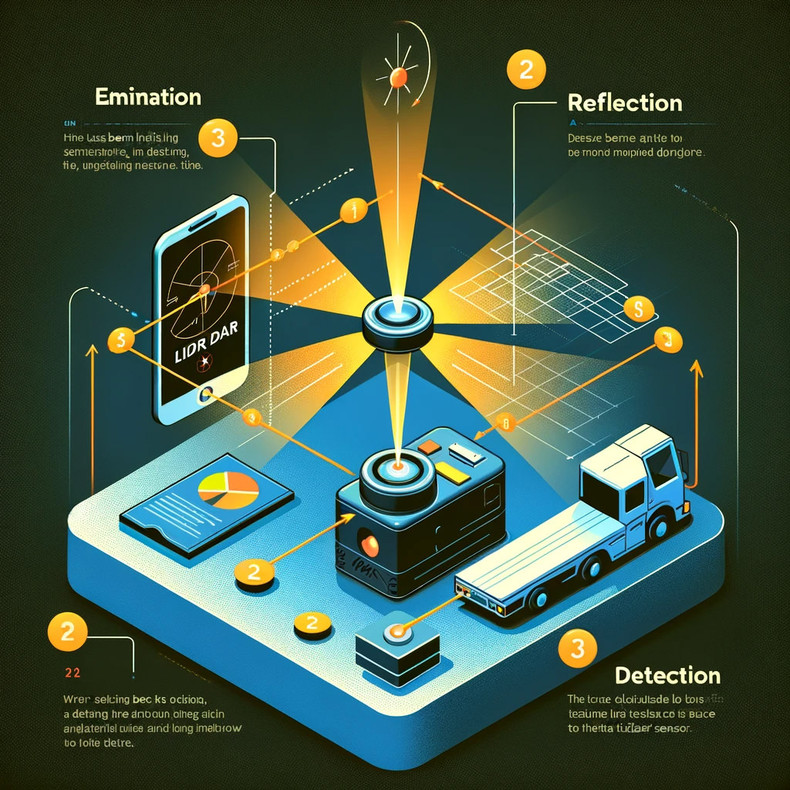
The working principle of 2D Lidar involves three main steps: emission, reflection, and detection. First, the device emits a laser beam towards a target. When the laser hits an object, it reflects back towards the Lidar sensor. The sensor then detects the reflected laser beams, and by calculating the time taken for the light to return, it determines the distance of the object from the sensor. Repeating this process rapidly across a wide area allows the creation of a detailed 2-dimensional map of the environment.
Applications of 2D Lidar
2D Lidar technology has wide applications across various sectors. In robotics, it is used for navigation, obstacle detection, and environment mapping, providing robots with the spatial data needed to move safely. Autonomous vehicles use it for similar reasons, aiding in safe driving by detecting nearby objects and pedestrians. Furthermore, in the field of geography and forestry, 2D Lidar aids in creating detailed maps of terrain and vegetation. These applications underline the technology’s significant role in improving safety, efficiency, and data collection in multiple industries.
Benefits of 2D Lidar
The primary benefits of using 2D Lidar technology include its accuracy and speed. It can measure distances and map environments with high precision, which is vital for navigation and safety in autonomous systems. Additionally, it operates effectively in a variety of lighting conditions, from bright daylight to complete darkness, unlike vision-based sensors that rely on ambient light. This reliability across conditions enhances its utility in outdoor and round-the-clock operations.
Limitations of 2D Lidar
Despite its advantages, 2D Lidar also faces certain limitations. Its performance can be hindered by extreme environmental conditions, such as heavy rain or fog, which scatter the laser beams and affect accuracy. Moreover, since it provides a two-dimensional view, it offers less depth information than 3D Lidar systems, which can limit its application in complex environments requiring detailed depth data.